Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -ray detection
-ray detectionKimura, Atsushi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Goko, Shinji; Harada, Hideo; Igashira, Masayuki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Kin, Tadahiro; Kino, Koichi*; Kitatani, Fumito; et al.
Proceedings of 2009 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (2009 NSS/MIC) (CD-ROM), p.138 - 143, 2009/10
To correct dead-time effect and measure high-precision neutron cross-section data, we have tested a dead-time correction method. In this method, random timing pulses are input to every pre-amplifiers of the Ge crystals via test-signal inputs. Both the random timing pulses and the other pulses originated from prompt  -rays are measured with our DAQ. At the same time, the inputs random pulses are counted with another system consisting of a fast timing amplifier, a CFD, and a counter. Because dead-time affects similarly both the random timing pulses and the measured prompt
-rays are measured with our DAQ. At the same time, the inputs random pulses are counted with another system consisting of a fast timing amplifier, a CFD, and a counter. Because dead-time affects similarly both the random timing pulses and the measured prompt  -rays, we can calculate dead-time by comparing the number of the input random pulses measured using the counter with the area of the peak due to the pulses from the pulse generator measured with our DAQ.
-rays, we can calculate dead-time by comparing the number of the input random pulses measured using the counter with the area of the peak due to the pulses from the pulse generator measured with our DAQ.
Kawachi, Naoki; Suzui, Nobuo; Ishii, Satomi; Ito, Sayuri; Ishioka, Noriko; Kikuchi, Kaori*; Tsukamoto, Takashi*; Kusakawa, Tomoyuki*; Fujimaki, Shu
Proceedings of 2009 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (2009 NSS/MIC) (CD-ROM), p.1257 - 1258, 2009/10
 germanium spectrometer for nuclear data measurements at J-PARC
germanium spectrometer for nuclear data measurements at J-PARCKin, Tadahiro; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Goko, Shinji; Harada, Hideo; Igashira, Masayuki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kino, Koichi*; Kitatani, Fumito; et al.
Proceedings of 2009 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (2009 NSS/MIC) (CD-ROM), p.1194 - 1197, 2009/10
For development of advanced reactors such as fast breeder reactors or accelerator driven systems, nuclear data of minor actinides (MAs) and long-lived fission products (LLFPs) are important for calculation of burning rates of fuels and transmutation rates to reduce the radio-toxicity of wastes. However, these data are insufficient at present in quantity and quality. To overcome/improve such a situation, we developed a 4 germanium spectrometer to measure neutron capture cross sections of MAs and LLFPs by time-of-flight measurements using pulsed neutron beams. At the conference, we will report details of the arrangement and characteristics of the spectrometer, such as detection efficiency, energy resolution and signal-to-background ratio, using results of measurement of standard sources. We will also show example of TOF spectra to report time resolution.
germanium spectrometer to measure neutron capture cross sections of MAs and LLFPs by time-of-flight measurements using pulsed neutron beams. At the conference, we will report details of the arrangement and characteristics of the spectrometer, such as detection efficiency, energy resolution and signal-to-background ratio, using results of measurement of standard sources. We will also show example of TOF spectra to report time resolution.
Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kimura, Atsushi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Toh, Yosuke; Kin, Tadahiro; Nakamura, Shoji; Oshima, Masumi
Proceedings of 2009 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (2009 NSS/MIC) (CD-ROM), p.2229 - 2233, 2009/10
To measure and improve differential linearity of flash ADCs used in integrated VME ADC modules, exponentially falling pulse-tails were digitized and counts of the resultant digital codes were recorded. The obtained histograms were fit to a function to deduce smoothly varying curves which should correspond to that obtained in the case of ideal linearity, and were compared to the fit value to calculate code width for each code. The obtained results show zigzag shaped deviation of about 10 % in magnitude from unity in the whole range and some large spikes which are as large as 100 %. A simple method is proposed to correct the nonlinearity using the ratios in post-processors following the ADCs. In the conference, the results of the correction will be presented.
 phosphors with radiators by irradiation of fast neutrons
phosphors with radiators by irradiation of fast neutronsSakasai, Kaoru; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Takakura, Kosuke; Konno, Chikara
Proceedings of 2009 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (2009 NSS/MIC), Vol.2, p.1422 - 1426, 2009/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:54.05(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Storage phosphors such as KCl:Eu with low
with low  -ray sensitivity were applied to detection of fast neutrons using polyethylene (PE) sheets as a proton generator that were set in front of the phosphors. The maximum PSL yields were obtained at a PE thickness of 3 mm when the neutron energy was 14.8 MeV. These experimental results well agreed with those by Monte Carlo simulation using PHITS code. Estimated PSL yields by
-ray sensitivity were applied to detection of fast neutrons using polyethylene (PE) sheets as a proton generator that were set in front of the phosphors. The maximum PSL yields were obtained at a PE thickness of 3 mm when the neutron energy was 14.8 MeV. These experimental results well agreed with those by Monte Carlo simulation using PHITS code. Estimated PSL yields by  -ray associated with fast neutron fields were negligible. This combination use of such phosphors and PE sheets will be usable for fast neutron monitoring or imaging in a high
-ray associated with fast neutron fields were negligible. This combination use of such phosphors and PE sheets will be usable for fast neutron monitoring or imaging in a high  -ray fields.
-ray fields.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Yasuda, Ryo; Katagiri, Masaki*; To, Kentaro; Sakasai, Kaoru; Birumachi, Atsushi; Ebine, Masumi; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of 2009 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (2009 NSS/MIC), Vol.2, p.1271 - 1273, 2009/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:54.05(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)A wavelength-shifting-fiber based neutron image detector with a spatial resolution of less 200  m was developed. The detector had a capability of clear imaging with a temporal resolution of several
m was developed. The detector had a capability of clear imaging with a temporal resolution of several  s. The detector equipped with a ZnS/
s. The detector equipped with a ZnS/ LiF scintillator where the scintillation light was read out with individual fibers based on a photon counting method. The fiber optic tapers (FOTs) were implemented in between the scintillator and the fibers to magnify a neutron image. The prototype detector that equipped with the FOTs exhibited the spatial resolution, which was improved by an order better compared that with the original detector. This kind of detector would be a quite unique and powerful tool for energy-selective neutron radiography at a pulsed source.
LiF scintillator where the scintillation light was read out with individual fibers based on a photon counting method. The fiber optic tapers (FOTs) were implemented in between the scintillator and the fibers to magnify a neutron image. The prototype detector that equipped with the FOTs exhibited the spatial resolution, which was improved by an order better compared that with the original detector. This kind of detector would be a quite unique and powerful tool for energy-selective neutron radiography at a pulsed source.
 Al
Al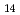 O
O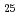 :Eu
:Eu ,Dy
,Dy
To, Kentaro; Sakasai, Kaoru; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Nagata, Shinji*; Tsuchiya, Bun*; Shikama, Tatsuo*
no journal, ,
Fluorescence and long lasting emission properties of Sr Al
Al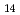 O
O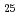 :Eu
:Eu ,Dy
,Dy were examined under proton irradiation by varying incident energy. The fluorescence spectra have three strong peaks at 400, 480, and 570 nm. The first two peaks are attributed to the luminescence of Eu and exhibit the long lasting property. The peak at 570 nm is attributed to the luminescence of Dy; it exhibits no luminescence after the irradiation has been stopped. The fluorescence intensity ratio of Eu/Dy exhibits incident energy dependence, and its value increases with an increase in the proton energy. Radiation damages show activator dependence, and Eu is more sensitive to incident particles than Dy is. Long-lasting emission is observed after the cessation of irradiation, and the decay time of the long-lasting emission is different for different irradiation fluence.
were examined under proton irradiation by varying incident energy. The fluorescence spectra have three strong peaks at 400, 480, and 570 nm. The first two peaks are attributed to the luminescence of Eu and exhibit the long lasting property. The peak at 570 nm is attributed to the luminescence of Dy; it exhibits no luminescence after the irradiation has been stopped. The fluorescence intensity ratio of Eu/Dy exhibits incident energy dependence, and its value increases with an increase in the proton energy. Radiation damages show activator dependence, and Eu is more sensitive to incident particles than Dy is. Long-lasting emission is observed after the cessation of irradiation, and the decay time of the long-lasting emission is different for different irradiation fluence.
To, Kentaro; Yamagishi, Hideshi*; Sakasai, Kaoru; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Soyama, Kazuhiko
no journal, ,
An improved micro-pixel detector element that showed high voltage tolerance was fabricated, and irradiation experiments using a Cf-252 neutron source were conducted on it. A gas-based neutron detection system capable of individual line readout, consisting of the developed detector element, gas chamber, amplifier-shaper-discriminator boards, and a fast data acquisition device, was constructed for the experiment. The micro-pixel gas chamber can identify signal-pulse peaks of neutrons and easily distinguish the neutron signals from background noises. The measured gas gain was approximately 280 at the supplied anode-cathode voltage of 670 V and total pressure of 0.5 MPa (0.45 MPa of  He and 0.05 MPa of CF
He and 0.05 MPa of CF ).
).
Soyama, Kazuhiko
no journal, ,
 H is a by product of Tritium production for use in nuclear weapons. Only the US and Russia are presently providing significant amounts of
H is a by product of Tritium production for use in nuclear weapons. Only the US and Russia are presently providing significant amounts of  H. With the end of the Cold War the
H. With the end of the Cold War the  H production from Tritium decay has been reduced significantly. However, since September 2001 the demand of
H production from Tritium decay has been reduced significantly. However, since September 2001 the demand of  H has increased drastically due to security programs launched in the US and other countries. This has led to a severe depletion of the existing
H has increased drastically due to security programs launched in the US and other countries. This has led to a severe depletion of the existing  H stockpile and caused the present shortage of
H stockpile and caused the present shortage of  H. With the upcoming new Spallation Sources and numerous projects for new instruments or upgrades at existing neutron scattering facilities the demand of
H. With the upcoming new Spallation Sources and numerous projects for new instruments or upgrades at existing neutron scattering facilities the demand of  H for neutron detectors has significantly increased. In this talk, a current status of construction of neutron scattering instruments and a problem of He3 shortage and alternative developments for neutron detection replacing
H for neutron detectors has significantly increased. In this talk, a current status of construction of neutron scattering instruments and a problem of He3 shortage and alternative developments for neutron detection replacing  H detectors at J-PARC will be reported.
H detectors at J-PARC will be reported.